Key Stage 4: GCSE Religious Studies
Curriculum Intent
Religious studies is an exciting subject that enables us to understand better the society in which we live and the wider world of which we are a part. In Religious Studies lessons you will learn strong reasoning, writing and critical thinking skills which are valued by all employers. You will take part in lively debates where you will learn about the views of others whilst also expressing your own opinions on the issues studied. Religious Studies develops key skills for any career that you choose to pursue. This video explains the importance Religious Studies and how studying Religious Studies could help your future. Click here
The GCSE Religious Studies course enables students to study two religions, Christianity and Islam in detail and four contemporary ethical themes, allowing students to explore a diverse choice of intriguing subjects. Students will be challenged with questions about belief, values, meaning, purpose and truth, enabling them to develop their own attitudes towards religious issues. Students will also gain an appreciation of how religion, philosophy and ethics form the basis of our culture. They will develop analytical and critical thinking skills, the ability to work with abstract ideas, leadership and research skills. All these skills will help prepare them for further study.
Aims and learning outcomes
This course enables the students to:
- develop their knowledge and understanding of religions and non-religious beliefs, such as atheism and humanism;
- develop their knowledge and understanding of religious beliefs, teachings and sources of wisdom and authority, including through their reading of key religious texts, other texts and scriptures of the religions they are studying;
- develop their ability to construct well-argued, well-informed, balanced and structured written arguments, demonstrating their depth and breadth of understanding of the subject;
- reflect on and develop their own values, belief, meaning, purpose, truth and their influence on human life;
- reflect on and develop their own values, beliefs and attitudes in the light of what they have learnt and contribute to their preparation for adult life in a pluralistic society and global community.
Throughout the course the students will write extended answers confidently and express their own points of view, whilst learning about the views of others and understanding why people have different opinions. They will confidently take part in class debates and discussions in order to understand and learn about local and world issues and to develop their listening, reading, writing and speaking skills which are vital in the world of work. The students will undertake a variety of questions worth 1, 2, 4, 5 and 12 marks on both examination papers. Up to three marks are awarded in respect of spelling, punctuation and grammar based on performance in the 12 mark extended writing questions on each examination paper.
The examinations will measure how students have achieved the following assessment objectives:
Demonstrate knowledge and understanding of religion and beliefs including:
- beliefs, practices and sources of authority
- influence on individuals, communities and societies
- similarities and differences within and/or between religions and beliefs.
Analyse and evaluate aspects of religion and belief, including their significance and influence.
Curriculum Overview
The students will study the AQA Religious Studies A Course. This qualification is linear which means that the students will sit two exams at the end of the course. The students will undertake the following two components:
- Component One: The study of religions: beliefs, teachings and practices
- Component Two: Thematic studies
Component One
Component one is examined in the first examination paper and is worth 50% of the final mark.
The students will study the following topics in relation to Christian beliefs and teachings:
- The nature of God
- God as omnipotent, loving and just
- The Oneness of God and the Trinity
- Christian beliefs about Creation
- The incarnation and Jesus, the Son of God
- The Crucifixion
- The Resurrection and Ascension
- Resurrection and life after death
- The afterlife and judgement
- Heaven and hell
- Sin and salvation
- The role of Christ in salvation
The students will study the following topics in relation to Christian practices:
- Worship
- Prayer
- The sacraments: baptism and Holy Communion
- Pilgrimage
- Celebrating Festivals
- The role of the church in the local community
- The place of mission and evangelism
- Church growth
- The importance of the worldwide church
- Christian persecution
- The Church’s response to world poverty
The students study the influence of the beliefs, teachings and practices studied on individuals, communities and societies. Common and divergent views within Christianity in the way beliefs and teachings are understood and expressed are considered throughout the course and the students refer to a range of different Christian perspectives in their answers including Catholic, Orthodox and Protestant.
The students will study the following topics in relation to Muslim beliefs and teachings:
- The Oneness of God and the supremacy of God’s will
- Key beliefs of Sunni Islam and Shi’a Islam
- The nature of God
- Angels
- Predestination
- Life after death
- Prophethood and Adam
- Ibrahim
- Muhammad and the Imamate
- The holy books in Islam
The students will study the following topics in relation to Muslim practices:
- The Five Pillars, the Ten Obligatory Acts and the Shahadah
- Salah: the daily prayers
- Sawm: fasting during Ramadan
- Zakah: almsgiving
- Hajj: Pilgrimage
- Jihad
- The festivals of Id-ul-Fitr and Id-ul-Adha
- The festival of Ashura
The students study the beliefs, teachings and practices of Islam and their basis in Islamic sources of wisdom and authority. They refer to scripture and other writings. Students study the influence of the beliefs, teachings and practices on individuals, communities and societies. Common and divergent views within Islam in the way beliefs and teachings are understood and expressed are studied throughout and the students refer to a range of different Muslim perspectives in their answers, including those from Sunni and Shi’a Islam.
Component Two
Component two is examined in the second examination paper and is worth 50% of the final mark. The students study four religious, philosophical and ethical themes.
Students will be aware of different religious perspectives on the issues studied within and / or between religious and non-religious beliefs such as atheism and humanism. The students study religious, philosophical and ethical arguments related to the issues raised, and their impact and influence on the modern world. They will show their understanding of religion through the application of teachings from religion and beliefs. The students will also make specific references to sources of wisdom and authority including scripture and/or sacred texts.
Students study religious teachings, and religious, philosophical and ethical arguments, relating to the issues that follow, and their impact and influence in the modern world. They are aware of contrasting perspectives in contemporary British society on all of these issues studied.
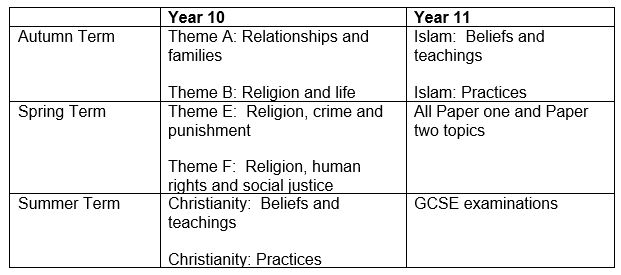
Theme A: Relationships and families
- Human sexuality
- Sexual relationships before and outside marriage
- Contraception and family planning
- Marriage
- Divorce and remarriage
- Religious teachings about the nature and purpose of families in the 21st century
- Religious attitudes to gender equality
Theme B: Relationships and life
- The origins of the universe
- The value of the world
- The use and the abuse of the environment
- Pollution
- The use and abuse of animals
- The origins of human life
- Abortion
- Euthanasia
- Death and the afterlife
Theme E: Religion, crime and punishment
- Crime and punishment
- Reasons for crime
- Lawbreakers and different types of crime
- Three aims of punishment
- Suffering and causing suffering to others
- The treatment of criminals – prison, corporal punishment and community service
- Forgiveness
- The death penalty
Theme F: Religion, human rights and social justice
- Social justice and human rights
- Prejudice and discrimination
- Religious freedom
- Wealth
- Poverty and its causes
- Exploitation of the poor
- Giving money to the poor
Knowledge of other cultures and world religious beliefs can be useful in many jobs where you are working with the public or communities. These include careers in law, medicine, counselling and social services, marketing, sales and advertising, catering and hospitality, leisure, sport and tourism, retail sales and customer services, education and training, nursing and service sector roles.
You could go on to study A-Level Religious Studies. There is a range of vocational qualifications linked to religious studies, including, travel and tourism, health and social care, childcare, uniformed public services and legal studies. There are apprenticeships associated with religious studies such as, leisure, travel and tourism and the arts, media and publishing.
Extra-curricular activities
Commit to six sessions are provided for students in Years 10 and 11 who are studying GCSE Religious Studies. In these sessions we focus on the examination techniques required to answer each type of question and the students take part in lively debates in order to consider issues from a variety of different perspectives. We also organise visits to places of worship in order for the students to develop further their knowledge of religious beliefs, teachings and practices.

